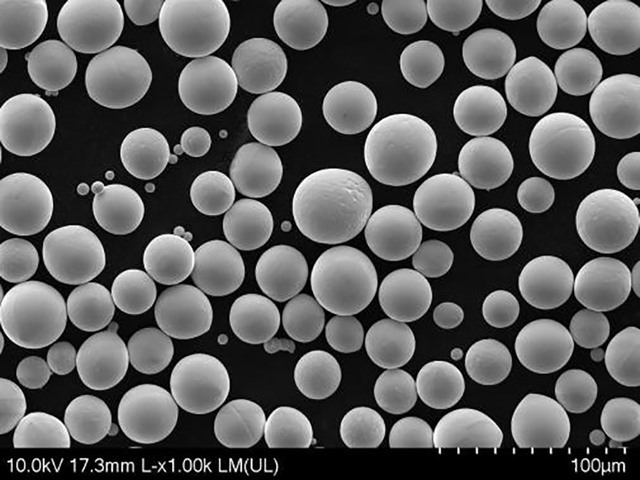
Titanium Zirconium Molybdenum (TZM) Alloy Powder
Spherical TZM powder is a premium molybdenum-based alloy powder composed of 99% Mo with 0.5% Ti and 0.08% Zr, enhanced with trace carbon for improved high-temperature strength and creep resistance. TZM Powder has superior strength at elevated temperatures, excellent creep resistance, and good oxidation resistance. TZM is commonly used in powder metallurgy, additive manufacturing, and high-temperature sintering applications.
Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of Titanium Zirconium Molybdenum alloy powder. Molybdenum series powders including Molybdenum Mo metal Powder, Molybdenum Rhenium Alloy Mo-Re Spherical Powder, and Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Powder are for sale in bulk.
Spherical TZM Molybdenum Powder
Formula | Titanium Zirconium Molybdenum, TZM Molybdenum |
Synonyms | Spherical TZM Molybdenum particle, spherical TZM Molybdenum powder, TZM Molybdenum Powder, TZM Molybdenum thermal spray powder, TZM Molybdenum gas atomized powder |
Appearance | Black Powder, spherical shape |
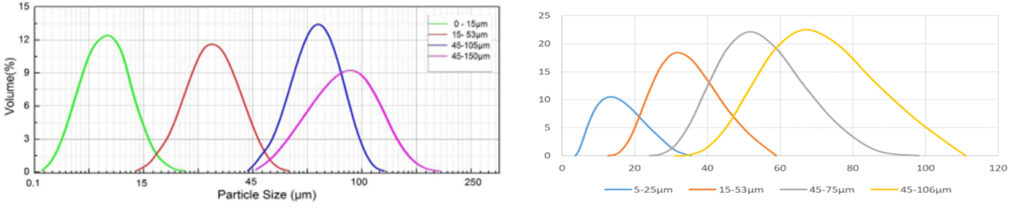
Particle Size | 15-53 um, 45-105 um, can be customized upon request |
Melting Point | 2623 °C |
Density | 10.22 g/cm 3 |
Tensile Strength, Ultimate | 760 MPa |
Elongationd | 15 |
Description of Spherical Molybdenum Alloy TZM Powder
Spherical Molybdenum TZM powder is a high-performance alloy powder composed of molybdenum with titanium (0.5%) and zirconium (0.08%). This powder is characterized by its spherical shape, which enhances flowability and packing density.
Spherical Molybdenum TZM powder has a spherical shape and a metallic gray color with a density of approximately 10.28 g/cm³ and a high melting point of around 2,620°C (4,748°F). The Titanium Zirconium Molybdenum alloy exhibits superior strength and creep resistance at elevated temperatures while maintaining good ductility for effective shaping. The Molybdenum TZM powder offers improved oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance due to the presence of titanium and zirconium, which form a protective oxide layer.
Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of Spherical Molybdenum TZM powder. We specialize in a comprehensive range of spherical powder products and possess extensive expertise in additive manufacturing (3D printing) industry. Molybdenum TZM powder is for sale at a competitive price.
TZM Powder Chemical Composition
| Element | Percentage | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum | ~97-98% | Provides the base material with high melting point and strength. |
| Titanium | ~0.5% | Enhances grain structure and strength. |
| Zirconium | ~0.08-0.12% | Improves ductility and oxidation resistance. |
| Carbon | ~0.01-0.04% | Adds strength by preventing grain growth. |
Spherical TZM powder Particle Size distribution
0-15μm, 15-53μm, 45-105μm, 45-150μm. (Various particle sizes can be customized)
Spherical Molybdenum-Ti-Zr alloy powder Applications
- Powder Metallurgy: TZM alloy powder is used in powder metallurgy to produce components that require high strength, excellent thermal stability, and resistance to creep and oxidation.
- Additive Manufacturing: Ideal for 3D printing, Spherical TZM Molybdenum alloy powder is utilized in additive manufacturing (e.g., Selective Laser Melting or Electron Beam Melting) to create highly precise parts with complex geometries.
- Metal Processing & Manufacturing: TZM alloy powder is utilized in metal processing and high-temperature furnaces where exceptional wear resistance and heat resistance are necessary.
- High-Temperature Tools: Titanium Zirconium Molybdenum alloy powder ability to maintain mechanical strength at high temperatures makes it ideal for cutting tools and mold inserts used in high-temperature environments.
Spherical TZM Powder Reference
Microstructure and mechanical properties of molybdenum-titanium-zirconium-carbon alloy TZM processed via laser powder-bed fusion
- Molybdenum, processed by laser powder-bed fusion (LPBF), is susceptible to hot cracking because segregated oxygen impurities significantly weaken grain boundaries through the formation of MoO2. The present study reports on the LPBF processing of the most important molybdenum alloy TZM, whose alloying elements—titanium, zirconium, and carbon—lead to particle and solid solution strengthening. Results of investigations into the resulting microstructure and mechanical properties when processing TZM by LPBF are presented. The alloying elements suppress the segregation of oxygen to the grain boundaries so that crack-free samples with a density of 99.7 ± 0.3% may be produced.
TZM is stronger than pure molybdenum and possesses a higher recrystallization temperature and better creep resistance. Commonly used in applications involving demanding mechanical loads, it’s recommended use temperature is between 1292°F (700°C) & 2552°F (1400°C).
The raw materials for producing TZM (Titanium-Zirconium-Molybdenum) alloy are:
- Molybdenum (Mo): The primary component of TZM, providing the base metal.
- Titanium (Ti): Typically added in amounts around 0.5%, contributing to the alloy’s high-temperature strength.
- Zirconium (Zr): Added in small quantities (around 0.08%) to enhance the alloy’s creep resistance and oxidation resistance.
These raw materials are mixed and processed to create TZM powder or billets, which are then used to manufacture high-performance components.
Studies have shown that TZM alloy oxidation rates are very slow and the alloy surface generates less volatile MoO2 when the temperature is below 400 C. The oxidation weight gaining increases rapidly by generating volatile MoO3 when temperatures were between 400 C and 750 C.