Tungsten Nickel Copper (W-6Ni-4Cu) Powder
Formula | W-6Ni-4Cu |
Synonyms | W-6Ni-4Co spherical particles, Tungsten Nickel Copper spherical powders, Tungsten Nickel Copper Powder |
Appearance | Black Powder, Spherical Morphology |
Particle Size | 0-45 um, 45-105 um, can be customized upon request |
Melting Point | 16.85~18.35 °C |
Density | 16.85~18.35 g/cm 3 |
Purity | 99.9% |
Apparent density | N/A |
Description of Tungsten Nickel Copper Spherical Powder
Tungsten nickel copper (W-Ni-Cu) spherical powder consists mainly of tungsten with nickel and copper, and is characterized by its spherical shape, which enhances flowability. It combines high density, hardness, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for applications like counterweights and radiation shielding. The powder is typically produced by atomization or powder metallurgy processes.
Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of spherical Tungsten nickel copper powder. We specialize in a comprehensive range of spherical powder products and possess extensive expertise in additive manufacturing (3D printing) industry. Tungsten alloy powder is for sale at a competitive price.
Chemical Composition
| Formula | W (%) | Ni (%) | Cu (%) |
| W-6Ni-4Cu | 90 | 6 | 4 |
| W-4.5Ni-3Cu | 92.5 | 4.5 | 3 |
| W-3.5Ni-1.5Cu | 95 | 3.5 | 1.5 |
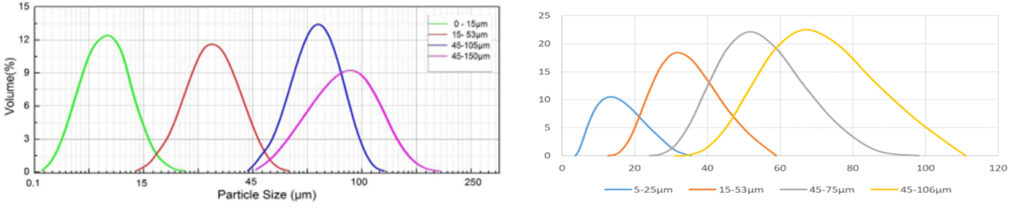
Particle Size distribution
0-15μm, 15-53μm, 45-105μm, 45-150μm. (Various particle sizes can be customized)
Applications
Tungsten nickel copper W-Ni-Cu spherical powder is used in various applications, including the production of high-density alloys for counterweights, radiation shielding, and aerospace components. It is also used in the manufacturing of components requiring high wear resistance and stability under high temperatures.
Tungsten Nickel Copper Spherical Powder Reference
Sintering of Tungsten and Tungsten Heavy Alloys of W–Ni–Fe and W–Ni–Cu: A Review
- This article reviews the recent research findings of consolidating tungsten and its alloys (W–Ni–Fe and W–Ni–Cu), from preparation of powder alloys to sintering of the compact. The advances in sintering are based on the objective of achieving good densification of the metal at lower temperature and at faster rate. The use of microwave sintering and spark plasma sintering techniques resulted in significant reduction in sintering time and producing products of good mechanical properties.

