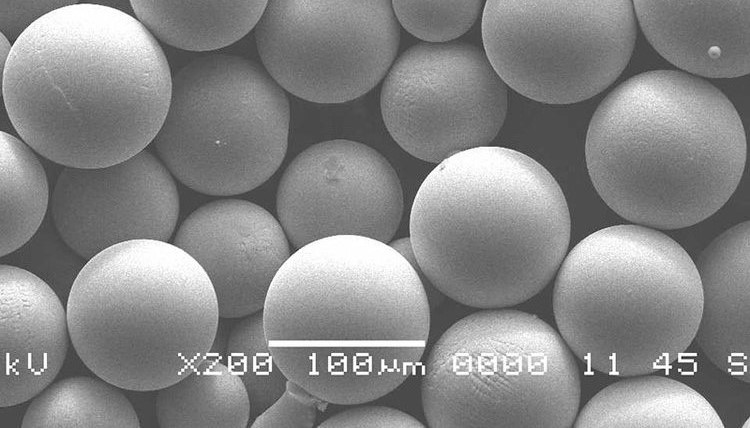
Nitinol Niti Round Powder (Spheroidal Particles)
Spherical Nickel Titanium alloy powder is a ball-shaped microns powder with a composition of 54%-57% w.t nickel (Ni) and titanium (Ti). Niti powder is also available in nano size, naming Nitinol nanopowder or Nitinol nanoparticles. The main manufacturing process includes Gas Atomized, Plasma Rotating Electrode Process, and Plasma Spheroidization. Pure Nitinol powder is widerly used in 3D printing process (additive manufacturing), including Laser Powder Bed Fusion, Electron Beam Melting, Selective Laser Melting, powder metallurgy, and thermal spraying.
Princeton Powder is a leading manufacturer of Nitinol powder. Nickel alloy powders including Inconel 625 Spherical Powder, Inconel 718 Spherical Powder, and Hastelloy C276 Powder are for sale in bulk in a competitive price.
Nickel titanium alloy Nitinol powder
Formula | Nitinol |
Synonyms | Nitinol spherical particles, nitinol spherical powders, Niti Powder, Nickel titanium Granules, Nitinol gas atomized powder |
Appearance | Black Powder |
Particle Size | 0-45 um, 45-105 um, can be customized upon request |
Melting Point | 1300°C |
Density | 6.45 g/cm 3 |
Tap Density | >4.0 g/cm³ |
Apparent density | >3.0 g/m3 |
Description of Nitinol Spherical Powder
Nitinol, also known as nickel-titanium alloy or memory alloy, is composed of nickel and titanium. It primarily comes in forms such as wire, sheet, tube, and powder. Key properties include the shape memory effect and superelasticity, allowing it to return to a preset shape upon heating or cooling and to recover its original shape after significant deformation. The shape memory temperature range typically lies between -20°C and 100°C, depending on the composition. Nitinol finds wide applications across various fields. In the medical industry, it is used to manufacture stents, dental braces, and surgical instruments. In aerospace, it is utilized for adaptive wings and temperature sensors.
Nitinol powder, also known as Nitinol alloy powder or memory alloy powder, is composed of nickel and titanium which often adheres to ASTM F2063 standards. nickel-titanium powder exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, is primarily used in 3D printing and additive manufacturing. Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of nitinol microns powder. We specialize in a comprehensive range of spherical powder products and possess extensive expertise in additive manufacturing (3D printing) industry.
Nitinol Spherical Powder Manufacturing method
Gas Atomization
Plasma Rotating Electrode Process (PREP)
Plasma Atomization
Mechanical Milling
Post-Processing: Powders are sieved into specific particle size distributions (e.g., 15–45 μm for 3D printing).
Nickel Titanium Powder Chemical Composition
Chemical Composition (wt%) | |||
Item | Ti | C | Ni |
| Nitinol | Bal. | 0.008 | 55.93 |
Oxygen: 587 ppm; Nitrogen: 49 ppm
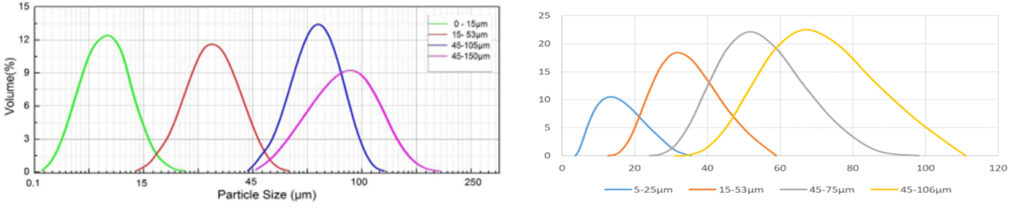
Particle Size distribution
0-15μm, 15-53μm, 45-105μm, 45-150μm. (Various particle sizes can be customized)
Applications
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Producing complex medical implants (e.g., stents) and aerospace components. Producing Nitinol part via nitinol powder of Selective Laser Melting, Electron Beam Melting, or Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Powder Metallurgy: Fabrication of high-density Nitinol parts for mechanical and thermal applications.
- Thermal Spraying: Coatings for wear resistance and biocompatibility.
Spherical niti Powder Scholar Articles
Laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) of NiTi alloy using elemental powders: the influence of remelting on printability and microstructure
- Additive manufacturing (AM) has now become a cost-effective, energy efficient and environmentally friendly fabrication process for low volume production. With the ongoing rapid reduction in three-dimensional (3D) printing costs, AM could soon become competitive with mainstream manufacturing forming strategies for mid-level runs as well.
- Nickel-titanium (NiTi), also referred to as nitinol, is one of the well-known, and frequently used, SMA materials.
Alloy Melting: Nickel and titanium are melted in a vacuum or inert gas environment.
Atomization: The molten alloy is rapidly cooled and broken into fine particles using high-pressure inert gas.
Screening and Classification: The powder is screened and classified by size.
Thermal Treatment: Additional treatments, like annealing, enhance properties.
Quality Control: Rigorous testing ensures compliance with standards like ASTM F2063 for medical applications.
Metal powders come in a variety of shapes, including disc-shaped, multiwalled, or fraction-shaped powders, droplets, elongated, spherical, agglomerated, satellited, irregular, angular, spongey, flaky, cylindrical, cubic, and acicular shaped powders, among others.
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF): Nitinol powder is spread in thin layers, and a laser or electron beam selectively fuses the powder to form the desired shape layer by layer.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): A laser sinters the Nitinol powder, solidifying it to create intricate and precise components directly from a digital model.
Binder Jetting: A binding agent is selectively deposited onto a bed of Nitinol powder to form the part layer by layer, followed by sintering to achieve full density