Atomized Iron Powder (Pure Iron Powder for Powder metallurgy and 3D printing)
Iron Powder includes Atomized Iron Powder (Pure Iron Powder), Reduced Iron Powder (Sponge Iron Powder), Iron Alloy Powder, Ultra-fine Iron Powder (Carbonyl Iron Powder),etc. The powder main used in powder metallurgy, additive manufacturing, magnetic components, chemical processes, filtration, and surface coatings for its versatile properties and applications.
Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of Iron spherical powder. We specialize in a comprehensive range of spherical powder products and possess extensive expertise in additive manufacturing (3D printing) industry. With our expertise, we are confident in supporting your projects effectively and provide you with reliable solutions.
Spherical Pure Iron (Fe) Metal Powder for 3D Printing
Formula | Iron, Fe |
Synonyms | Iron spherical particles, spherical Fe powders, Reduced Iron Powder, Sponge Iron Powder, Iron thermal spray powder, Pure Iron gas atomized powder, Carbonyl Iron Powder |
Appearance | Black Powder |
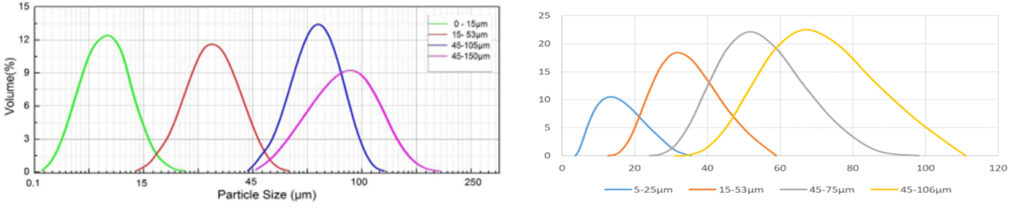
Particle Size | 0-45 um, 45-105 um, can be customized upon request |
Melting Point | 1535 °C |
Density | 7.89 g/cm 3 |
Tap Density | 6.5 g/cm³ |
Apparent density | 3.0 – 3.7 g/cm3 |
Description of Iron (Fe) Metal Powder (Reduced powder sponge and Carbonyl Iron Powder)
Pure Iron (Fe) Metal Spherical Powder is typically >99.9% pure, with particle sizes ranging from 10 µm to 100 µm. It is produced via atomization, resulting in fine, spherical particles with a density of around 7.87 g/cm³. This powder is commonly used in additive manufacturing, powder metallurgy, and the production of soft magnetic materials.
Reduced Iron Powder is produced by reducing iron oxide (Fe2O3 or Fe3O4) with hydrogen or carbon, resulting in a highly pure, fine powder with a typical purity of 98-99%. It has a soft, malleable nature and is often used in applications like powder metallurgy, magnetic materials, and as a catalyst in chemical reactions. The powder is sensitive to oxidation and should be stored in airtight containers to maintain its quality.
Carbonyl Iron Powder is produced through the carbonylation process, where iron reacts with carbon monoxide to form iron pentacarbonyl, which is then decomposed into fine, high-purity iron powder. It typically has a purity of 99.9% or higher and consists of very fine, spherical particles with a high surface area. This powder is commonly used in electromagnetic applications, soft magnetic components, and as a precursor for high-performance metal alloys
Iron Fe powder is available in various grades, including Atomized Iron Powder, Reduced Iron Powder (Iron Sponge), and Carbonyl Iron Powder. Due to its high reactivity with oxygen, it must be stored in a dry, controlled environment to prevent oxidation. Applications include electronics, biomedical fields, and high-conductivity components. They are available in bulk with a competitive price.
Chemical Composition/Particle Size of Iron Fe particles (Iron Microns Powder)
Iron (Fe)≧99.8%
Oxygen (O)≤300 ppm
Nitrogen (N)≤300 ppm
0-15μm, 15-53μm, 45-105μm, 45-150μm. (Various particle sizes can be customized)
Application of Iron Powder(manufactured via reducing or carbonylation process)
- Powder Metallurgy: Used to create strong, complex sintered components for automotive parts, machinery, and tools.
- Additive Manufacturing: Essential in 3D printing for high-precision metal parts, suitable for prototyping and small-batch production.
- Magnetic Applications: Used in soft magnetic components for inductors and transformers in electrical devices.
- Chemical Industry: Acts as a catalyst and reagent in various reactions and the production of ferrites.
- Filtration and Absorption: Applied in filters and purifiers for water treatment and air purification.
- Surface Coatings: Used in thermal spraying for wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Iron Fe metal Powder Scholar Articles
- Sintering temperature and shrinkage has declined considerably with the decrease in the powder size and as a result the strength increases. High strength for products made by smaller powders under high pressures and low sintering temperatures using lubricated frame wall are obtained. SEM pictures from the fracture junctions of the samples show the decrease in porosity due to the close impact of the smaller powder size.
Iron powder has several uses; for example production of magnetic alloys and certain types of steels. Iron powder is formed as a whole from several other iron particles. The particle sizes vary anywhere from 20-200 μm. The iron properties differ depending on the production method and history of a specific iron powder.
Due to its excellent magnetic properties, the electrolytic iron powder can also be used for making ferromagnetic cores. In soft magnetic applications, high purity iron powder is specifically used in ignition system components, electric motor components, solenoids, and inductors.
Commercial iron powders are classified in three types, reduced iron powder, atomized iron powder, and electrolytic iron powder, depending on the production method, and are used in various applications, taking advantage of their respective properties.

