Plasma-Spheroidized Hafnium Powder (Hafnium Micron Powder)
Spherical Hafnium Powder, also called Spheroidized Hafnium Powder or Hafnium Spheres, is generally manufactured via gas atomization. 15-45μm and 53-105 um spherical Hf Powder is commonly available for sale. Our Hafnium powder has low oxygen content, good sphericity and excellent flowability. Gas-Atomized Hafnium Powder is widely used for additive manufacturing LPBF and EBM process.
Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of Hafnium series powder. Hafnium powders including Hafnium oxide powder, Hafnium Disilicide HfSi2 Powder, and Hafnium Hydride Powder are for sale in bulk.
Spherical Hafnium Hf Powder
Formula | Hafnium, Hf |
Synonyms | Hafnium Hf powder, Spherical Hafnium Powder (Hf Powder) |
Appearance | Gray solid |
Particle Size | 1-10 um, 15-45 um, 45-105 um, can be customized upon request |
Melting Point | 2222°C |
Purity | 99.6% |
Specific Gravity | 13.3 |
CAS Number | 7440-58-6 |
Description of Spherical Hafnium Hf Powder
Spherical hafnium (Hf) powder is a fine, metallic powder characterized by its spherical shape, which enhances flowability and packing density. It has a high melting point of around 2,222°C and excellent strength, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. The powder is often used in the aerospace industry for components that require heat resistance and in nuclear reactors due to its neutron-absorbing properties. Additionally, spherical hafnium powder is utilized in various electronic applications and specialty alloys for its unique properties.
Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of Spherical hafnium (Hf) powder. We specialize in a comprehensive range of Hf products and possess extensive expertise in additive manufacturing (3D printing) industry. Hf Spherical powder is for sale at a competitive price.
Chemical Composition
Grade | Chemical Composition (%) | |||||||
Hf | Hf | Zr | Al | Cr | Mg | Ni | ||
| Bal | 0.05 | 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 | |||
Pb | C | Cd | Sn | Ti | Fe | |||
0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0130 | |||
Cl | Si | Mn | Co | Mo | Sb | |||
0.0001 | 0.0100 | 0.0010 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
Cu | Bi | H | O | N | C | |||
0.0010 | 0.0001 | 0.0200 | 0.1000 | 0.0050 | 0.0050 | |||
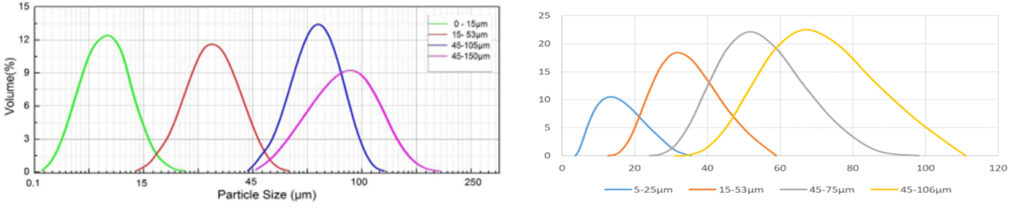
Particle Size | 0-15μm, 15-53μm, 45-105μm, 45-150μm. (Various particle sizes can be customized) | |||||||
Physical Properties | ||||||||
Apparent Density (g/cm3) | Tap Density (g/cm3) | Hall Flow Rate (s/50g) | ||||||
>6.50 | >7.50 | <10.0 | ||||||
Particle Size distribution
0-15μm, 15-53μm, 45-105μm, 45-150μm. (Various particle sizes can be customized)
Applications
- Hafnium Powder for LPBF 3D Printing
- Hf Powder for EBM
- Hafnium Powder used for neutron absorption
- Used in electronic devices and thin-film coatings.
Spherical Hafnium Hf Powder Reference
Hf metal powder synthesis via a chemically activated combustion-reduction process
- The present study demonstrates the synthesis of fine hafnium (Hf) metal powders via a chemically activated combustion synthesis (CS) approach, which develops temperatures in the range of 1000–1600 °C. The current CS approach can be employed to obtain Hf powders with a single-crystalline hexagonal close-packed (hcp) structure in addition to high compositional uniformity and average particle sizes ranging from 0.05 to 2.0 μm. The mechanism of Hf particle formation can be understood by analyzing the process thermodynamics, including adiabatic temperatures and equilibrium reaction phases.
Hafnium and zirconium are transition metals. They resemble each other because they have similar chemical properties. The key difference between hafnium and zirconium is that hafnium has comparatively a low density, whereas zirconium has a high density.
Hafnium has good neutron-absorbing properties, and hence it is used in control rods in nuclear reactors. While hafnium nitride is the most refractory of all the metal nitrides, hafnium carbide is the most refractory of all the binary materials.
- High Melting Point: Hafnium has a melting point of 2,233°C, making it suitable for high-temperature environments.
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, especially in reactive environments.
- Thermal Conductivity: Good thermal conductivity, beneficial for heat management applications.
- Reactivity: Can react with oxygen and other elements at elevated temperatures.

