Spherical Pure Copper Powder
Formula | Cu |
Synonyms | Pure copper spherical particles, Copper Cu metal spherical powders, Cu Powder, Copper thermal spray powder, Copper gas atomized powder |
Appearance | Brown Powder |
Particle Size | 0-45 um, 45-105 um, can be customized upon request |
Melting Point | 1083 °C |
Density | 8.94 g/cm 3 |
Tap Density | >5.1 g/cm³ |
Apparent density | >4.2 g/m3 |
Description of Copper Cu Spherical Powder
Copper powder is a versatile metal powder prized for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability. It comes in various forms and sizes, each tailored to specific industrial needs. Copper powder’s diverse forms and superior properties make it essential in applications such as 3D printing, electronics, catalysis, metal injection molding, and coatings, enhancing both traditional and cutting-edge manufacturing processes.
- Ultrafine and Nano Copper Powder: Ultrafine Cu powder ranges from micrometers to sub-micrometer sizes, while nano copper powder particles are typically less than 100 nanometers, offering unique properties for advanced applications.
- Pure Copper Powder: This high-purity powder, often exceeding 99% copper content, is ideal for conductive applications.
- Electrolytic Copper Powder: Known for its high purity and dendritic shape, this powder is perfect for electrical uses.
- Spherical Copper Powder: Atomized to create smooth, spherical particles, it ensures good flowability and packing density, beneficial for 3D printing and additive manufacturing.
- Copper Fine Powder and 325 Mesh Powder: Fine powders, including 325 mesh, are used in metal injection molding and sintering.
- Atomized Copper Powder: Produced by atomizing molten copper, resulting in irregular or spherical particles suitable for powder metallurgy.
- Nanopowder: Ultra-small copper particles are used in high-tech applications like electronics and advanced coatings.
- Sintered and Welding Powder: Used for creating sintered parts and as welding powder for metal joining and repair.
Princeton Powder is a leading supplier of Cu metal powder, offering it for sale at competitive prices. We specialize in a comprehensive range of spherical copper powder products and have extensive expertise in the additive manufacturing (3D printing) industry. With our knowledge and experience, we confidently support your projects and provide reliable solutions.
Chemical Composition
| Chemical Composition by ICP-AES: | Wt % |
| Cu | Remainder |
| Fe | <0.01 |
| Al | <0.01 |
| Ca | <0.001 |
| Mo | <0.001 |
| Si | <0.005 |
| Ni | <0.01 |
| Mg | <0.01 |
| Gas Impurities | |
| O | ≤0.05 |
| N | ≤0.008 |
| C | ≤0.001 |
Particle Size distribution
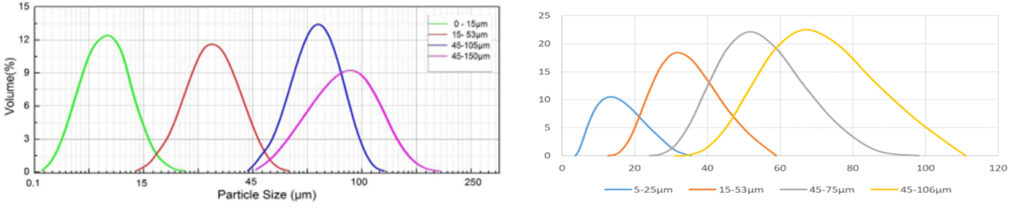
0-15μm, 15-53μm, 45-105μm, 45-150μm. (Various particle sizes can be customized)
Applications
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
- Electronics:
- Powder Metallurgy: Utilized to create sintered components with high strength and complex geometries.
- Catalysts: Used in processes like hydrogenation and dehydrogenation.
- Metal Injection Molding (MIM):
- Welding and Brazing:
- Coatings and Paints:
- Filtration:
- Magnetic Applications
Spherical Copper Cu Powder Reference
Preparation of micron size copper powder with chemical reduction method
- The preparation of micron size copper powder with chemical reduction method was investigated. The copper powder having excellent dispersibility was prepared when sodium metaphosphate was employed as dispersion agent.
Copper is used in metallurgy, chemical industry, machinery, electronics, aerospace, and other fields. When combined with a solid surface, fine copper powder can form a smooth protective layer; thus, it is often used as a lubricating oil additive, which can reduce friction, filling, and scratches.
Pure copper powder is used in the electrical and the electronics industries because of its excellent electrical and thermal conductivities. Alloyed with tin, zinc, nickel and other elements, copper in powder form is used in structural parts and friction materials.
The hydrometallurgy process can be used to produce copper powder from cement copper, concentrates or scrap copper. The copper is leached from these materials with sulfuric acid or ammoniacal solutions and the pregnant solution is separated from the residue by filtration.

